1,What are the bipolar and unipolar characteristics of a motor?
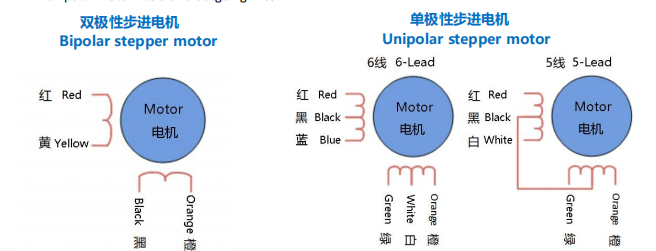
Bipolar Motors:
Our bipolar motors generally have only two phases, phase A and phase B, and each phase has two outgoing wires, which are separate winding. There is no connection between the two phases. Bipolar motors have 4 outgoing wires.
Unipolar motors:
Our unipolar motors generally have four phases. On the basis of two phases of bipolar motors, two common lines are added.
If common wires are connected together, the outgoing wires are 5 wires.
If common wires are not connected together, the outgoing wires are 6 wires.
An unipolar motor has 5 or 6 outgoing lines.
2,What is the maximum operating frequency/maximum pull-out frequency?
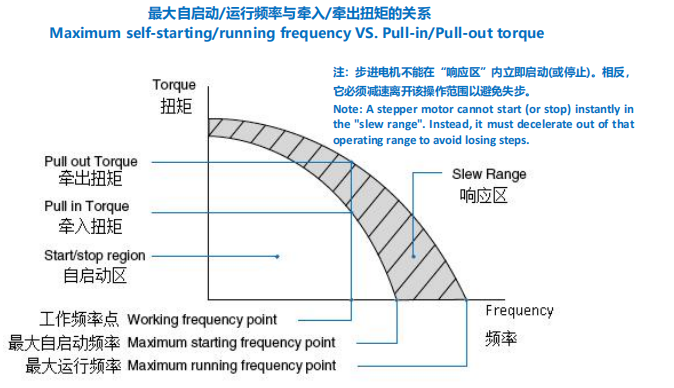
Maximum running frequency/Maximum pull-out frequency
Maximum running frequency, also known as maximum slewing frequency / maximum pull-out frequency, is the maximum frequency at which the motor can keeps rotating under a certain driving form, voltage and rated current, without adding a load.
Due to the inertia of the rotor, a rotating motor requires less torque to spin compared to a stationary motor, so maximum running frequency will be bigger than maximum self-starting frequency.
3,What are the pulling torque and pulling torque of a stepper motor?
Pull-out torque
Pull-out torque is the maximum torque that can be delivered without losing steps. It reaches its
maximum at the lowest frequency or speed, and decreases as frequency increases. If the load on the
stepping motor during rotation increases beyond the pull-out torque, the motor will fall out of step
and accurate operation will not be possible.
Pull-in torque
Pull-in torque is the maximum torque at which a motor can start rotating at a given frequency from
stationary status. The stepper cannot start rotation with the load torque exceeding the pull-in torque.
Pull-in torque is smaller than pull-out torque, due to inertia of motor’s rotor.
4,What is the self positioning torque of a stepper motor?
Detent torque is the torque present in the unenergized state due to the interaction of the permanent
magnets and stator teeth. A noticeable disturbance or cogging can be felt by rotating the motor by
hand.Generally, a stepper motor will lose synchronization when the pull-out torque is exceeded due to
overload. Motors are often selected and evaluated using pull-out torque values above the
requirements for the application to prevent lost counts or motor stalls.
5,What are the driving modes of stepper motors?
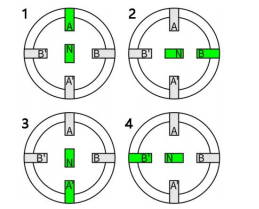
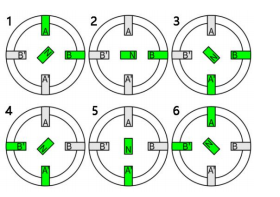
Wave / one-phase-on driving works with only one phase
turned on at a time, shown in the illustration right side. When the drive energizes pole A (south pole) shown in green,it attracts the north pole of the rotor. Then when the driveenergizes B and switches A off, the rotor rotates 90 ° and this continues as the drive energizes each pole one at a time.
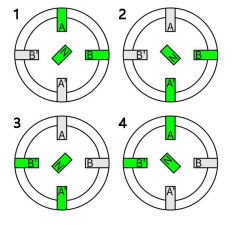
2-2 Phases Driving has its name because two phases are on at a time. If the drive energizes both A and B poles as south poles (shown in green), then the rotor’s north pole attracts to both equally and aligns in the middle of the two. As the energizing sequence continues on like this, the rotor continuously ends up aligning in-between two poles. 2-2 phases driving gets no finer resolution than one-phase on, but it does produce more torque. This is the driving method we use most often in our tests, also known as “full step driving”.
1-2 phase driving is named after the driver switches between 1-phase and 2-phases of excitation. The driver energizes pole A, then energizes both poles A and B, then energizes pole B, then energizes both poles A and B, and so forth. (Shown in the green part in the right side) 1-2 phase driving provides finer motion resolution. When 2 phases are energized, motor has more torque. Here’s a reminder: Torque ripple is a concern, because it might cause resonance and vibration. Compared with full-step driving/2-2-phase driving, step angle of 1-2-phase drive is only halved, and it takes twice of steps to rotate one revolution , so 1-2 phase driving is also called “half step driving” 1-2 phase drive can also be considered as the most basic subdivision drive.
6,How to choose a suitable stepper motor?
For the best selection, those
basic theoretical rules have to be respected:
The first task is to select the right stepper motor for the application.
1. Select the motor based on the highest torque/ speed point required by the application (selection based on the worst case)
2. Use at least 30% design margin from the published torque vs. speed curve (pull-out curve).
3. Ensure that the application will not not be stalled by external events.
Post time: Sep-09-2025