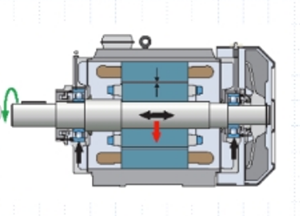
● The role of rolling bearings in motors
1、Support the rotor.
2, Rotor positioning.
3, to ensure that the size of the air gap, uniform from the shaft to the seat to transfer the load to protect the motor from low speed to high speed operation.
4, reduce friction, reduce loss.
What needs to be discerned clearly is that the bearings in the motor do not bear the torque load of the motor, so what is generally referred to as the no-load state of the motor load has little effect on the bearings.
● Friction
1, and the roughness of the contact surface, hardness, and lubrication conditions – the coefficient of friction.
2, static friction > sliding friction > rolling friction.
3, sliding friction coefficient 0.1-0.2.
4, rolling friction coefficient 0.001-0.002.
5, fluid dynamics friction – plain bearings.
Bearings reduce friction mechanically and lubrication reduces friction chemically. Therefore, it is necessary to understand friction before understanding bearings.
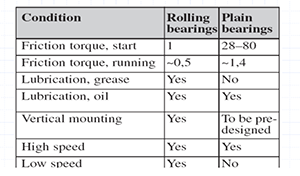
● Rolling and Plain Bearings
Rolling bearings
1, The motor can be placed horizontally or vertically.
2. They can be operated in a wide range of speeds.
Slide Bearing
1, The placement of the motor needs to be pre-designed.
2, Can only be operated within the designed operating speed range.
3, Large starting torque, cannot run at low speed.
Rolling bearings and plain bearings for motors, in addition to the different friction mode, there are also differences in application.
● Comparison of rolling bearings and plain bearings
The biggest difference between rolling bearings and plain bearings is the difference in friction. The difference in friction brings about a difference in application conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to choose the type of bearing according to the application conditions.
●Commonly used bearings in industrial motors
1, Deep groove ball bearings DGBB.
2, Cylindrical Roller Bearing CRB.
3, CARB.
4, Insulated bearings INSOCOAT.
5, Ceramic bearings.
6, Encoder Bearing.
● Main characteristics of deep groove ball bearings
1,Excellent axial and radial load carrying capacity makes it the first choice for small and medium-sized motors.
2,Pre-load can be applied by wave spring to make the motor run more quietly and reliably.
3, different sealing methods to adapt to different needs.
4,Wide temperature grease can be used to run in a wider temperature range.
Deep groove ball bearings are the most common type of bearings in electric motors, accounting for more than 70% of the entire industrial motor bearing usage.
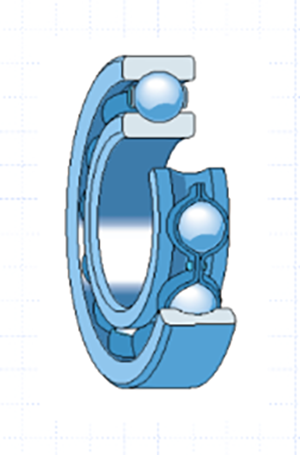
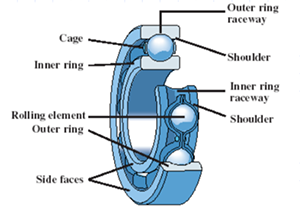
●Composition of deep groove ball bearings
1, outer ring
2, inner ring
3、Cage
4、Rolling body
5、Dust cover (sealing cover)
Understanding the components of bearings facilitates engineering expression for engineers.
●Bearing Cage
A Stamped steel cage: strong, high temperature resistant.
B Nylon cage: High running speed, low noise, running temperature up to 120 degrees.
temperature up to 120 degree Celsius.
C Machined copper cage: Robust, can be used in vibration environment.
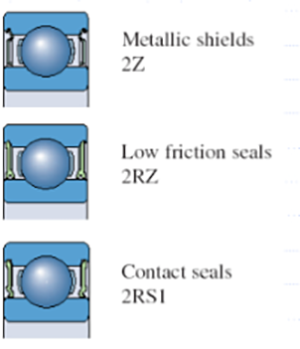
●Bearing seals
1, 27 – Same speed rating as open bearings, medium sealing effect.
2, 2RZ – Good sealing effect with the same speed rating as open bearings.
3, 2RS1(H)-Best sealing effect, lower speed rating than the first two.
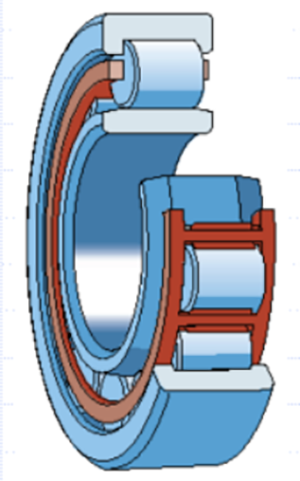
●Cylindrical roller bearings
1, have better load bearing capacity than deep groove ball bearings.
2, Especially suitable for the belt drive end of medium and large motors.
3, Various designs can be used as non-locating bearings or locating bearings.
4, Large mounting errors are not allowed.
Cylindrical rollers have these characteristics, resulting in the selection of the type according to these characteristics. Specific selection needs to consider the load capacity, speed capacity, life calibration and other factors.
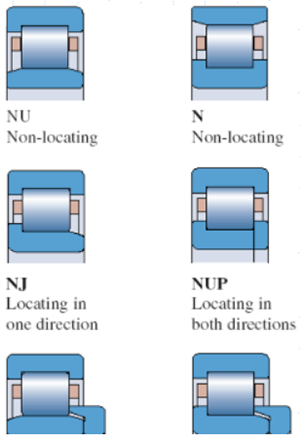
●Cylindrical roller bearings in many different designs
1, NU type – non-locating bearings with outer ring having a rim.
2, N type – inner ring has a gear edge, non-locating bearings.
3, N] type – the outer ring has a gear edge inner ring has a gear edge on one side, one-way positioning.
4, NUP – than N] type more than a movable edge, two-way positioning.
Different types of cylindrical roller bearings actually have different characteristics. So there are also different application scenarios. For example, N and NU, in some of the use of the process, in some of the lubrication bearing characteristics, there are differences.
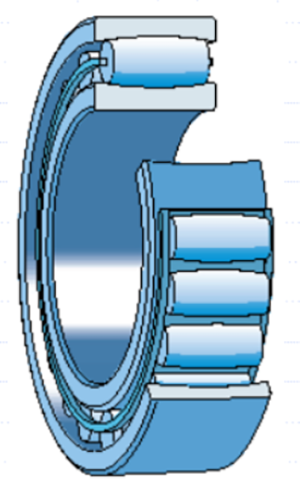
●CARB bearings
1, can be applied to the occasion where there is a relatively large misalignment between the shaft and the centre line of the bearing ((can be self-aligning).
2, They can replace cylindrical roller bearings as non-locating bearings in industrial motors.
3, Inner and outer full circle can be used with transition fit.
●INSOCOAT
1, Developed from plain bearings.
2, There is an insulating plating layer of aluminium oxide and resin on the inner or outer ring to prevent shaft current from damaging the bearing.
3, It should be placed at the non-driving end of the motor.
4, Mounting and dismounting methods are the same as those for ordinary bearings.
●Hybird bearing
1, The rolling body of ceramic bearing is silicon nitride ceramic material.
2, The rolling body is insulated, eliminating overcurrent in the bearing.
3, Ceramic material has high hardness and is not sensitive to temperature change, so it can have longer time in lubrication.
4, In order to ensure the insulation effect, this bearing is not equipped with dust cover.
Note: We only sell motors, here just introduce motor bearings.
Post time: Feb-20-2024