Stepper motors can be used for speed control and positioning control without the use of feedback devices (i.e. open-loop control), so this drive solution is both economical and reliable. In the automation equipment, instruments, stepper drive has been very widely used. But many users of technical personnel on how to choose the appropriate stepper motor, how to make the best performance of the stepper drive or have more questions. This paper discusses the selection of stepper motors, focusing on the application of some stepper motor engineering experience, I hope that the popularization of stepper motors in automation equipment to play a role in reference.
1、Introduction of stepper motor
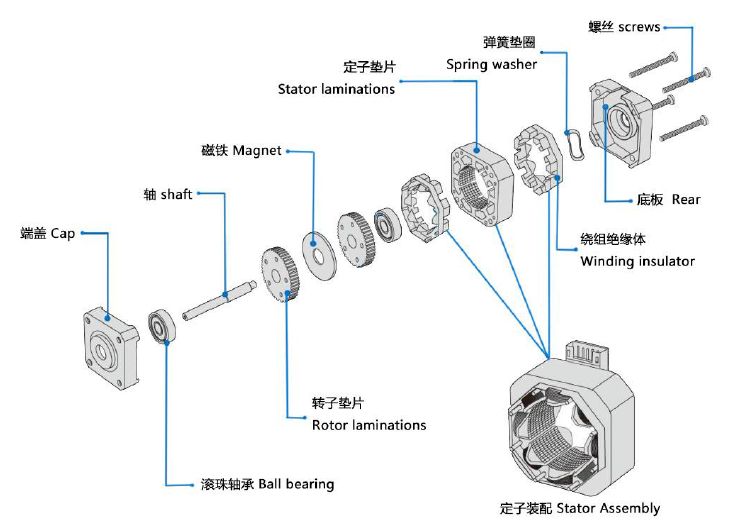
The stepper motor is also known as a pulse motor or step motor. It advances by a certain angle every time the excitation state is changed according to the input pulse signal, and remains stationary at a certain position when the excitation state remains unchanged. This allows the stepper motor to convert the input pulse signal into a corresponding angular displacement for output. By controlling the number of input pulses you can accurately determine the angular displacement of the output in order to achieve the best positioning; and by controlling the frequency of the input pulses you can accurately control the angular speed of the output and achieve the purpose of speed regulation. In the late 1960s, a variety of practical stepper motors came into being, and the last 40 years have seen rapid development. Stepper motors have been able to DC motors, asynchronous motors, as well as synchronous motors alongside, becoming a basic type of motor. There are three types of stepper motors: reactive (VR type), permanent magnet (PM type) and hybrid (HB type). The hybrid stepper motor combines the advantages of the first two forms of stepper motor. The stepper motor consists of a rotor (rotor core, permanent magnets, shaft, ball bearings), a stator (winding, stator core), front and rear end caps, etc. The most typical two-phase hybrid stepper motor has a stator with 8 large teeth, 40 small teeth and a rotor with 50 small teeth; a three-phase motor has a stator with 9 large teeth, 45 small teeth and a rotor with 50 small teeth
2、Control principle
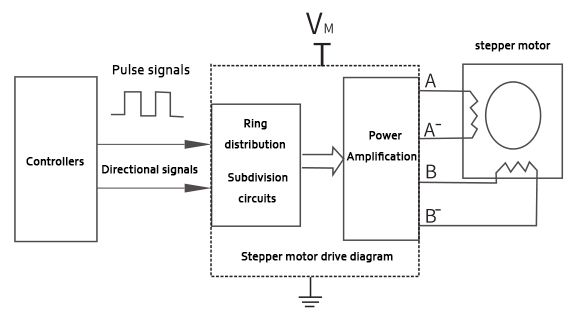
The stepper motor cannot be directly connected to the power supply, nor can it directly receive electrical pulse signals, it must be realized through a special interface - the stepper motor driver to interact with the power supply and controller. The stepper motor driver is generally composed of a ring distributor, and a power amplifier circuit. The ring divider receives the control signals from the controller. Each time a pulse signal is received the output of the ring divider is converted once, so the presence or absence and frequency of the pulse signal can determine whether the stepper motor speed is high or low, accelerating or decelerating to start or stop. The ring distributor must also monitor the direction signal from the controller to determine whether its output state transitions are in positive or negative order, and thus determine the stepper motor's steering.
3、Main parameters
①Block number: mainly 20, 28, 35, 42, 57, 60, 86, etc.
②Phase number: the number of coils inside the stepper motor, stepper motor phase number generally has two-phase, three-phase, five-phase. China uses two-phase stepper motors mainly, three-phase also has some applications. Japan is more often used five-phase stepper motors
③Step angle: corresponding to a pulse signal, the angular displacement of the motor rotor rotation. Stepper motor step angle calculation formula is as follows
Step angle = 360° ÷ (2mz)
m the number of phases of a stepper motor
Z the number of teeth of the rotor of a stepper motor.
According to the above formula, the step angle of two-phase, three-phase and five-phase stepper motors is 1.8°, 1,2° and 0.72° respectively
④ Holding torque: is the torque of the stator winding of the motor through the rated current, but the rotor does not rotate, the stator locks the rotor. Holding torque is the most important parameter of stepper motors, and is the main basis for motor selection
⑤ Positioning torque: is the torque required to turn the rotor with external force when the motor does not pass current. The torque is one of the performance indicators to evaluate the motor, in the case of other parameters are the same, the smaller the positioning torque means that the "slot effect" is smaller, the more beneficial to the smoothness of the motor running at low speed torque frequency characteristics: mainly refers to the drawn out torque frequency characteristics, the motor stable operation at a certain speed can withstand the maximum torque without losing step. The moment-frequency curve is used to describe the relationship between the maximum torque and speed (frequency) without loss of step. The torque frequency curve is an important parameter of the stepper motor and is the main basis for motor selection.
⑥ Rated current: the motor winding current required to maintain the rated torque, the effective value
4、Selecting points
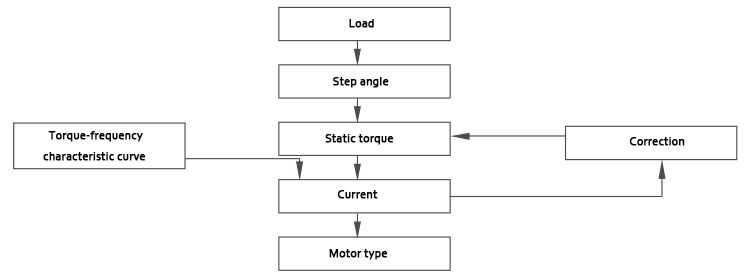
Industrial applications used in the stepper motor speed up to 600 ~ 1500rpm, higher speed, you can consider closed-loop stepper motor drive, or choose a more appropriate servo drive program stepper motor selection steps (see the figure below).
(1) Choice of step angle
According to the number of phases of the motor, there are three kinds of step angle: 1.8° (two-phase), 1.2° (three-phase), 0.72° (five-phase). Of course, the five-phase step angle has the highest accuracy but its motor and driver are more expensive, so it is rarely used in China. In addition, the mainstream stepper drivers are now using subdivision drive technology, in 4 subdivision below, subdivision step angle accuracy can still be guaranteed, so if the step angle accuracy indicators alone from the consideration, five-phase stepper motor can be replaced by two-phase or three-phase stepper motor. For example, in the application of some kind of lead for 5mm screw load, if a two-phase stepping motor is used and the driver is set at 4 subdivisions, the number of pulses per revolution of the motor is 200 x 4 = 800, and the pulse equivalent is 5 ÷ 800 = 0.00625mm = 6.25μm, this accuracy can meet most of the application requirements.
(2) Static torque (holding torque) selection
Commonly used load transmission mechanisms include synchronous belts, filament bars, rack and pinion, etc. Customers first calculate their machine load (mainly acceleration torque plus friction torque) converted to the required load torque on the motor shaft. Then, according to the maximum running speed required by the electric flowers, the following two different use cases to choose the appropriate holding torque of the stepper motor ① for the application of the required motor speed of 300pm or less: if the machine load is converted to the motor shaft required load torque T1, then this load torque is multiplied by a safety factor SF (generally taken as 1.5-2.0), that is, the required stepper motor holding torque Tn ②2 for For applications requiring a motor speed of 300pm or more: set the maximum speed Nmax, if the machine load is converted to the motor shaft, the required load torque is T1, then this load torque is multiplied by a safety factor SF (usually 2.5-3.5), which gives the holding torque Tn. Refer to Figure 4 and select a suitable model. Then use the moment-frequency curve to check and compare: on the moment-frequency curve, the maximum speed Nmax required by the user corresponds to the maximum lost step torque of T2, then the maximum lost step torque T2 should be more than 20% larger than T1. Otherwise, it is necessary to select a new motor with a larger torque, and check and compare again according to the torque frequency curve of the newly selected motor.
(3) The larger the motor base number, the larger the holding torque.
(4) according to the rated current to select the matching stepper driver.
For example, the rated current of a motor 57CM23 is 5A, then you match the drive's maximum allowable current of more than 5A (please note that it is the effective value rather than the peak), otherwise if you choose a maximum current of only 3A drive, the maximum output torque of the motor can only be about 60%!
5, application experience
(1) stepper motor low frequency resonance problem
Subdivision stepper drive is an effective way to reduce the low frequency resonance of stepper motors. Below 150rpm, the subdivision drive is very effective in reducing the vibration of the motor. Theoretically, the larger the subdivision, the better the effect on reducing stepper motor vibration, but the actual situation is that the subdivision increases to 8 or 16 after the improvement effect on reducing stepper motor vibration has reached the extreme
In recent years, there have been anti-low-frequency resonance stepper drivers listed at home and abroad, Leisai's DM, DM-S series of products, the anti-low-frequency resonance technology. This series of drivers uses harmonic compensation, through the amplitude and phase matching compensation, can greatly reduce the low frequency vibration of the stepper motor, to achieve low vibration and low noise operation of the motor.
(2) The impact of stepper motor subdivision on positioning accuracy
Stepper motor subdivision drive circuit can not only improve the smoothness of the device movement, but also can effectively improve the positioning accuracy of the equipment. Tests show that:In the synchronous belt drive motion platform, stepper motor 4 subdivision, the motor can be accurately positioned at each step.
Post time: Jun-11-2023