Linear stepper motor, also known as linear stepper motor, is a magnetic rotor core by interacting with the pulsed electromagnetic field generated by the stator to produce rotation, linear stepper motor inside the motor to convert rotary motion into linear motion. Linear stepper motors can do linear motion or linear reciprocating motion directly. If a rotary motor is used as the power source to convert into linear motion, gears, cam structures and mechanisms such as belts or wires are required. The first introduction of linear stepper motors was in 1968, and the following figure shows some typical linear stepper motors.

Basic principle of externally driven linear motors
The rotor of an externally driven linear stepper motor is a permanent magnet. When current flows through the stator winding, the stator winding generates a vector magnetic field. This magnetic field drives the rotor to rotate at a certain angle, so that the direction of the rotor's pair of magnetic fields coincides with the direction of the stator's magnetic field. When the stator's vector magnetic field rotates by an angle. The rotor also rotates at an angle with this magnetic field. For each electrical pulse input, the electric rotor rotates by one angle and moves one step forward. It outputs an angular displacement proportional to the number of pulses input and a speed proportional to the pulse frequency. Changing the order of winding energization reverses the motor. So the stepper motor rotation can be controlled by controlling the number of pulses, frequency and the order of energizing the motor windings of each phase.
The motor uses a screw as the outgoing axis, and an external drive nut is engaged with the screw outside the motor, taking some way to prevent the screw nut from turning to relative to each other, thus achieving linear motion. The result is a greatly simplified design that allows the use of linear stepper motors directly for precise linear motion in many applications without the installation of an external mechanical linkage.
Advantages of externally driven linear motors
Precision linear screw stepper motors can replace cylinders in some applications, achieving advantages such as precise positioning, controllable speed, and high accuracy. Linear screw stepper motors are used in a wide range of applications including manufacturing, precision calibration, precision fluid measurement, precise position movement, and many other areas with high precision requirements.
▲High precision, repeatable positioning accuracy up to ±0.01mm
Linear screw stepping motor reduces the problem of interpolation lag due to the simple transmission mechanism, positioning accuracy, repeatability and absolute accuracy.It is easier to achieve than the "rotary motor + screw". The repeat positioning accuracy of the ordinary screw of the linear screw stepping motor can reach ±0.05mm, and the repeat positioning accuracy of the ball screw can reach ±0.01mm.
▲ High speed, up to 300m/min
The speed of linear screw stepping motor is 300m/min and acceleration is 10g, while the speed of ball screw is 120m/min and acceleration is 1.5g. And the speed of linear screw stepping motor will be further improved after successfully solving the heat problem, while the "rotary The speed of "servo motor & ball screw" is limited in speed, but it is difficult to improve more.
High life and easy maintenance
The linear screw stepping motor is suitable for high precision because there is no contact between the moving parts and fixed parts due to the mounting gap and no wear due to the high speed reciprocating motion of the movers. The ball screw cannot guarantee the accuracy in the high-speed reciprocating motion, and the high-speed friction will cause the wear of the screw nut, which will affect the accuracy of the motion and cannot meet the demand for high precision.
Selection of external drive linear motor
When making linear motion related products or solutions, we suggest engineers to focus on the following points.
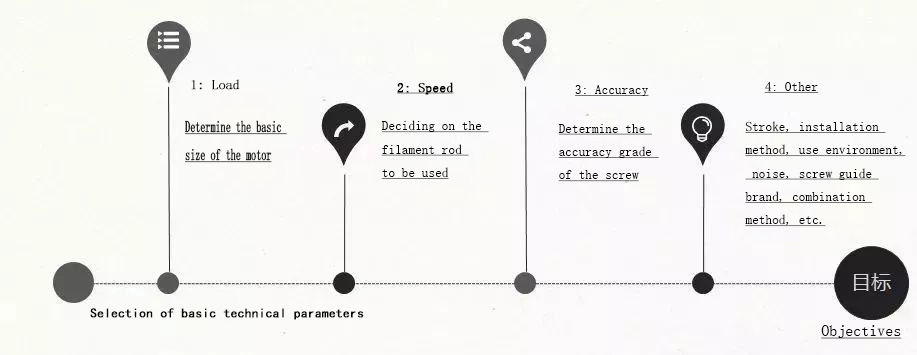
1. What is the load of the system?
The load of the system includes static load and dynamic load, and often the size of the load determines the basic size of the motor.
Static load: the maximum thrust that the screw can withstand at rest.
Dynamic load: the maximum thrust that the screw can withstand when it is in motion.
2. What is the linear running speed of the motor?
The running speed of the linear motor is closely related to the lead of the screw, one revolution of the screw is one lead of the nut. For low speed, it is advisable to choose a screw with a smaller lead, and for high speed, it is advisable to choose a larger screw.
3. What is the accuracy requirement of the system?
Screw accuracy: the accuracy of the screw is generally measured by the linear accuracy, i.e. the error between the actual travel and the theoretical travel after the screw rotates for a bitter dry circle.
Repeat positioning accuracy: repeat positioning accuracy is defined as the accuracy of the system to be able to reach the specified position repeatedly, which is an important indicator for the system.
Backlash: backlash of the screw and nut at rest when the two axial relative moveable amount. As the working time increases, the backlash will also increase due to wear. Compensation or correction of backlash can be achieved by the backlash elimination nut. When bi-directional positioning is required, backlash is a concern.
4. Other selections
The following issues also need to be considered in the selection process: Is the mounting of the linear stepper motor in accordance with the mechanical design? How will you connect the moving object to the nut? What is the effective stroke of the screw rod? What kind of drive will be matched?

Post time: Nov-16-2022
